This page was generated from
jupyter-notebook/nb_03time-lapse.ipynb.
Interactive online version:
 .
Download notebook.
.
Download notebook.
Time-lapse inversion
In this notebook we will see how to use ResIPy API to do a time-lapse inversion (difference).
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import os
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.relpath('../src')) # add here the relative path of the API folder
testdir = '../src/examples/dc-2d-timelapse/'
from resipy import Project
API path = /media/jkl/data/phd/resipy/src/resipy
ResIPy version = 3.4.6
cR2.exe found and up to date.
R3t.exe found and up to date.
cR3t.exe found and up to date.
Then we can import all the dataset. Note that they should all be in the same directory and will be sorted according to alphabetical order.
[2]:
k = Project(typ='R2')
k.createTimeLapseSurvey(testdir + 'data/')
Working directory is: /media/jkl/data/phd/resipy/src/resipy
clearing dirname
3/3 imported
[3]:
k.surveys # to display the list of the surveys object
[3]:
[<resipy.Survey.Survey at 0x7f16c84a38e0>,
<resipy.Survey.Survey at 0x7f16417ca410>,
<resipy.Survey.Survey at 0x7f16417ca1a0>]
The inversion is seamlessly the same. It will automatically take the first survey os background model. Invert it in a specific ref directory inside the working directory and then invert the other datasets.
[4]:
k.invert(parallel=True) # takes a while because it invert all the surveys together
Creating triangular mesh...done (1786 elements)
Writing .in file and protocol.dat... Matching quadrupoles between pairs of (background, surveyX) for difference inversion...done in 0.0044s
done
------------ INVERTING REFERENCE SURVEY ---------------
>> R 2 R e s i s t i v i t y I n v e r s i o n v4.10 <<
>> D a t e : 03 - 12 - 2023
>> My beautiful survey
>> I n v e r s e S o l u t i o n S e l e c t e d <<
>> Determining storage needed for finite element conductance matrix
>> Generating index array for finite element conductance matrix
>> Reading start resistivity from res0.dat
>> R e g u l a r i s e d T y p e <<
>> L i n e a r F i l t e r <<
>> L o g - D a t a I n v e r s i o n <<
>> N o r m a l R e g u l a r i s a t i o n <<
>> D a t a w e i g h t s w i l l b e m o d i f i e d <<
Processing dataset 1
Measurements read: 190 Measurements rejected: 0
Geometric mean of apparent resistivities: 0.51162E+02
>> Total Memory required is: 0.003 Gb
Iteration 1
Initial RMS Misfit: 30.43 Number of data ignored: 0
Alpha: 428.484 RMS Misfit: 1.62 Roughness: 1.735
Alpha: 198.884 RMS Misfit: 1.24 Roughness: 2.403
Alpha: 92.314 RMS Misfit: 0.98 Roughness: 3.134
Step length set to 1.00000
Final RMS Misfit: 0.98
Cannot fit quadratic through step lengths
Final RMS Misfit: 0.98
Solution converged - Outputing results to file
Calculating sensitivity map
Processing dataset 2
End of data: Terminating
--------------------- MAIN INVERSION ------------------
0/2 inversions completedors
All ok
>> R 2 R e s i s t i v i t y I n v e r s i o n v4.10 <<
>> D a t e : 03 - 12 - 2023
>> My beautiful survey
>> I n v e r s e S o l u t i o n S e l e c t e d <<
>> R 2 R e s i s t i v i t y I n v e r s i o n v4.10 <<
>> D a t e : 03 - 12 - 2023
>> My beautiful survey
>> I n v e r s e S o l u t i o n S e l e c t e d <<
>> Determining storage needed for finite element conductance matrix
>> Determining storage needed for finite element conductance matrix
>> Generating index array for finite element conductance matrix
>> Generating index array for finite element conductance matrix
>> Reading start resistivity from Start_res.dat
>> R e g u l a r i s e d T y p e <<
>> L i n e a r F i l t e r <<
>> T r u e - D a t a I n v e r s i o n <<
>> D i f f e r e n c e R e g u l a r i s a t i o n <<
>> D a t a w e i g h t s w i l l b e m o d i f i e d <<
>> Reading start resistivity from Start_res.dat
>> R e g u l a r i s e d T y p e <<
>> L i n e a r F i l t e r <<
>> T r u e - D a t a I n v e r s i o n <<
>> D i f f e r e n c e R e g u l a r i s a t i o n <<
>> D a t a w e i g h t s w i l l b e m o d i f i e d <<
Processing dataset 1
Measurements read: 344 Measurements rejected: 0
Geometric mean of apparent resistivities: 0.70496E+02
>> Total Memory required is: 0.006 Gb
Processing dataset 1
Measurements read: 344 Measurements rejected: 0
Geometric mean of apparent resistivities: 0.53348E+02
>> Total Memory required is: 0.006 Gb
Iteration 1
Iteration 1
Initial RMS Misfit: 14.53 Number of data ignored: 0
Initial RMS Misfit: 2.54 Number of data ignored: 0
Alpha: 614.804 RMS Misfit: 0.80 Roughness: 0.255
Step length set to 1.00000
Final RMS Misfit: 0.80
Alpha: 389.880 RMS Misfit: 4.56 Roughness: 10.525
Alpha: 180.966 RMS Misfit: 4.47 Roughness: 18.225
Final RMS Misfit: 1.03
Solution converged - Outputing results to file
Calculating sensitivity map
Processing dataset 2
End of data: Terminating
1/2 inversions completed Alpha: 83.997 RMS Misfit: 4.61 Roughness: 29.147
Step length set to 1.00000
Final RMS Misfit: 4.47
Updated data weights
Iteration 2
All ok
Initial RMS Misfit: 3.33 Number of data ignored: 0
Alpha: 114.863 RMS Misfit: 1.91 Roughness: 13.030
Alpha: 53.315 RMS Misfit: 1.36 Roughness: 18.983
Alpha: 24.747 RMS Misfit: 1.15 Roughness: 25.850
Alpha: 11.486 RMS Misfit: 1.29 Roughness: 33.615
Step length set to 1.00000
Final RMS Misfit: 1.15
Attempted to update data weights and caused overshoot
treating as converged
Solution converged - Outputing results to file
Calculating sensitivity map
Processing dataset 2
End of data: Terminating
2/2 inversions completed
----------- END OF INVERSION IN // ----------
3/3 results parsed (3 ok; 0 failed)
All ok
Note that we can visualize the different inverted sections using R2.showResults(index=0, attr='Resistivity(log10)').
[5]:
k.showResults(index=0, attr='Resistivity(log10)', contour=False, vmin=1.5, vmax=2)
k.showResults(index=1, attr='Resistivity(log10)', contour=False, vmin=1.5, vmax=2)
k.showResults(index=2, attr='Resistivity(log10)', contour=False, vmin=1.5, vmax=2)
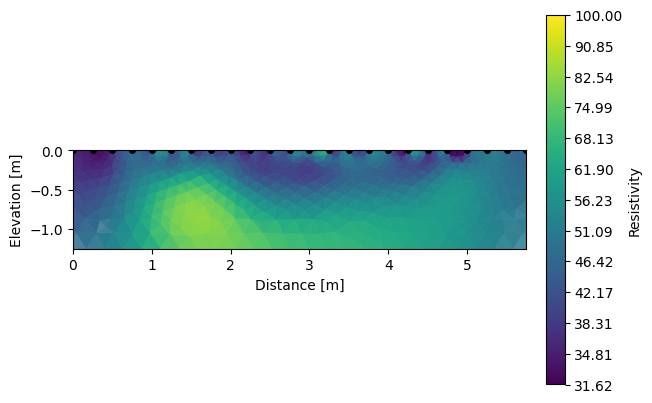
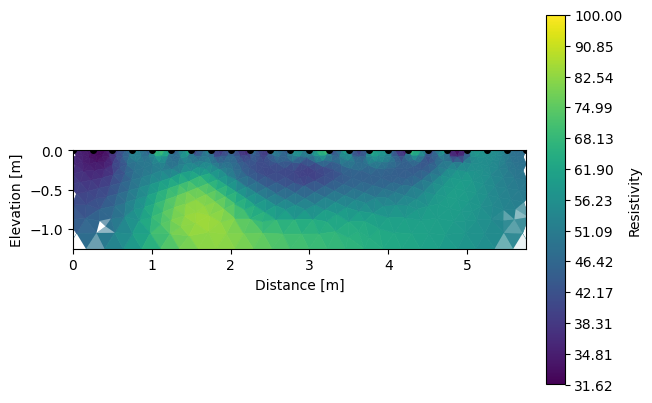
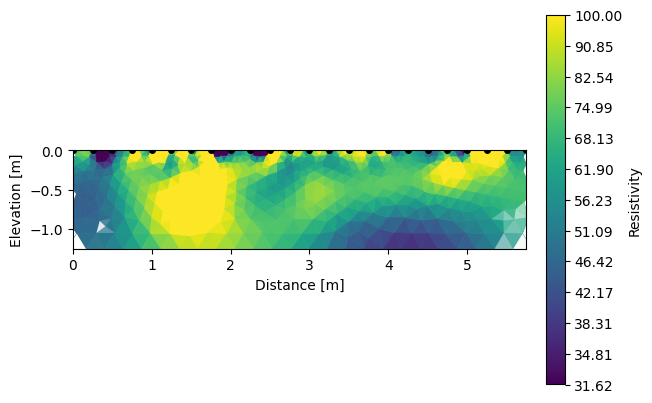
We can also look for the differences between each survey.
[6]:
# the differnces are in percent in reference to the backround survey (index=0)
k.showResults(index=1, attr='difference(percent)', contour=False, vmin=0, vmax=100)
k.showResults(index=2, attr='difference(percent)', contour=False, vmin=0, vmax=100)
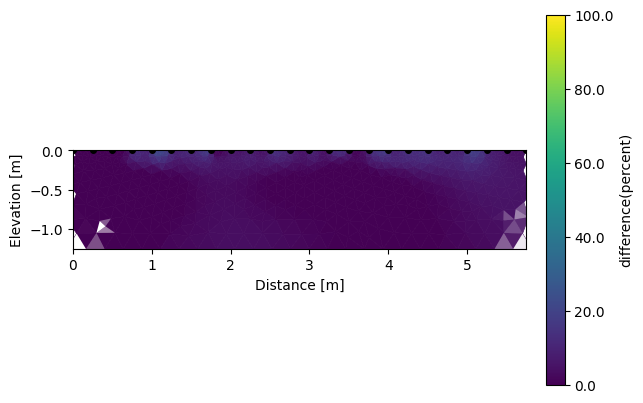
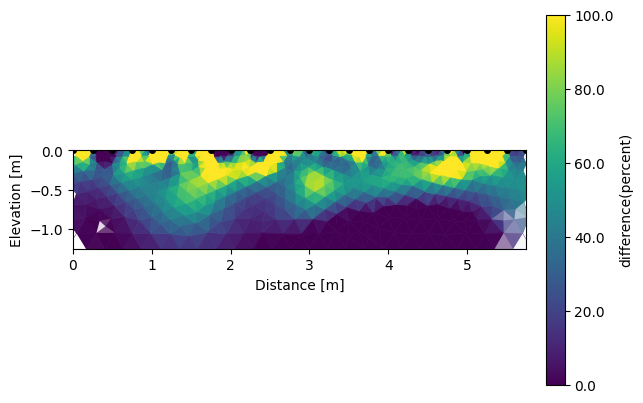
Like this we can observe a deeper positive change (drying) during the growth season of wheat mainly due to the root water uptake.
[ ]: